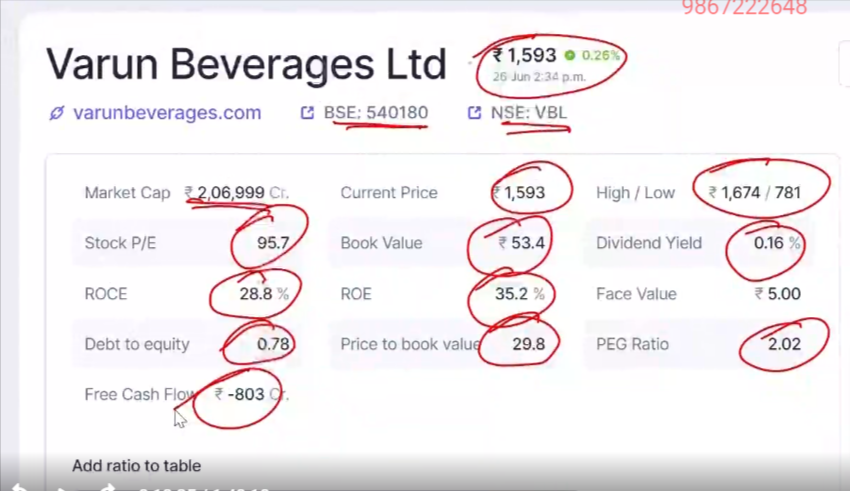
- Market Cap (₹2,06,999 Cr.):
- Explanation: Market Capitalization is the total market value of a company’s outstanding shares. It is calculated by multiplying the current share price by the total number of outstanding shares. It provides an overview of the company’s size in the stock market.
- Stock P/E (95.7):
- Explanation: The Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio measures a company’s current share price relative to its per-share earnings. A high P/E might indicate that the stock is overvalued, or investors expect high growth rates in the future.
- ROCE (28.8%):
- Explanation: Return on Capital Employed (ROCE) indicates the efficiency and profitability of a company’s capital investments. It is calculated by dividing Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) by Capital Employed. A higher ROCE indicates efficient use of capital.
- Debt to Equity (0.78):
- Explanation: This ratio compares a company’s total liabilities to its shareholder equity. It shows how much debt is used to finance the company’s assets relative to the value of shareholders’ equity. A lower ratio is generally better, indicating less reliance on debt.
- Free Cash Flow (₹-803 Cr.):
- Explanation: Free Cash Flow (FCF) represents the cash generated by a company after accounting for capital expenditures necessary to maintain or expand its asset base. A negative FCF indicates that the company is spending more on investments than it is generating from its core operations.
- Current Price (₹1,593):
- Explanation: This is the current trading price of the company’s stock. It shows what investors are willing to pay per share in the market.
- Book Value (₹53.4):
- Explanation: Book Value refers to the net asset value of a company. It is calculated as total assets minus total liabilities and represents the intrinsic value of the company.
- ROE (35.2%):
- Explanation: Return on Equity (ROE) measures a company’s profitability by comparing net income to shareholders’ equity. A higher ROE indicates that the company is effectively generating income from its equity base.
- Price to Book Value (29.8):
- Explanation: The Price-to-Book (P/B) ratio compares the market value of a company’s stock to its book value. A higher P/B ratio might indicate that the stock is overvalued relative to its assets.
- High / Low (₹1,674 / 781):
- Explanation: This represents the highest and lowest prices at which the stock has traded over a certain period, usually the past year. It provides a range of the stock’s price volatility.
- Dividend Yield (0.16%):
- Explanation: Dividend Yield shows how much a company pays out in dividends each year relative to its share price. It is a measure of the income generated by owning shares, expressed as a percentage of the current stock price.
- Face Value (₹5.00):
- Explanation: Face Value is the nominal value of a share as stated in the company’s books. It is important for determining the stock’s book value and is often used in calculating dividends and stock splits.
- PEG Ratio (2.02):
- Explanation: The Price/Earnings to Growth (PEG) ratio is used to determine a stock’s value while taking into account the company’s earnings growth. A PEG ratio of 1 is considered fair value, less than 1 is undervalued, and more than 1 might be overvalued considering the growth rate.
These metrics are crucial for evaluating the financial health, performance, and valuation of the company in the stock market.